Report Identifies 5 Key Elements of Effective Care Management for Seniors
Four Case Studies Identify a Blueprint of Successful Models of Care Management in Medicare Advantage
A new report released today by the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care on behalf of the Better Medicare Alliance (BMA) identifies five key elements essential to effective care management to meet the needs of Medicare beneficiaries.
For Immediate Release
Washington, D.C. – A new report released today by the Robert Graham Center for Policy Studies in Family Medicine and Primary Care on behalf of the Better Medicare Alliance (BMA) identifies five key elements essential to effective care management to meet the needs of Medicare beneficiaries.
The report, “Bright Spots in Care Management”, examines four case studies of successful models of care management in Medicare Advantage, the managed care option under Medicare.
The release of the report follows ongoing interest in Congress to modernize Medicare to improve disease management and care coordination for patients living with one or more chronic conditions. In May, the Senate Finance Committee unanimously voted to approve S 870, the “Creating High-Quality Results and Outcomes Necessary to Improve Chronic (CHRONIC) Care Act of 2017.” Today, the House Ways and Means Committee will hold a hearing on improving integrated and coordinated care for Medicare beneficiaries.
“This is essentially a blueprint for effective care management in Medicare Advantage that should be a helpful tool for plans and providers. In light of policymakers’ attention to the critical challenge in Medicare to improve care for those with chronic conditions, this report contributes important information essential to improving health outcomes and managing costs for Medicare beneficiaries,” said Allyson Y. Schwartz, BMA President and CEO.
The report highlights how the financial framework of risk based, capitated payments under Medicare Advantage enables emphasis on improving care coordination, early intervention, care transitions, and effective secondary interventions for Medicare beneficiaries.
“We don’t have a lot of data about the aspects of care management that are most effective, but we know there are places that do it well. We learned from them that capitated payment in Medicare Advantage allows organizations to be creative in structuring their programs,” said Winston Liaw, MD, Medical Director of the Robert Graham Center.
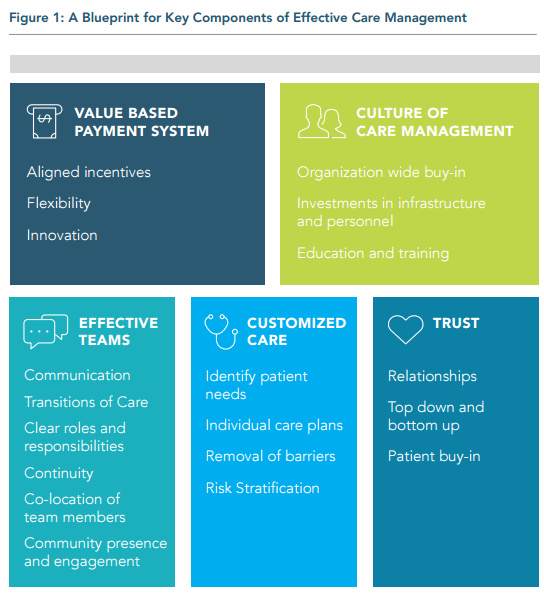
FIVE KEY ELEMENTS TO EFFECTIVE CARE MANAGEMENT:
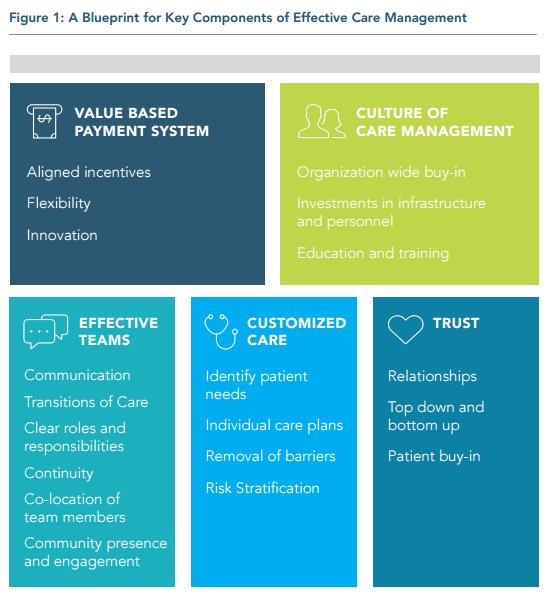
- A Value-Based Payment System with aligned incentives that promotes flexibility and innovation.
- A Culture of Care Management that invests infrastructure and personnel resources to create and maintain a new culture organization wide.
- Effective Teams that co-locate care managers with care providers to enhance communication.
- Customized Care that identifies patient needs and uncovers resources, competencies, goals, preferences, and values of the patients.
- Trust that cultivates patient buy-in.
The report compiled by researchers from the Robert Graham Center examined four successful models of care management through extensive interviews with Medicare Advantage and care management experts, an environmental scan and field visits to the following Medicare Advantage financed care management programs:
- CareMore, a Medicare Advantage payer and provider aligned model that utilizes teams to manage chronic diseases and transitions of care for 80,000 Medicare Advantage beneficiaries in California, Nevada, Arizona, Ohio, Virginia, Georgia, Iowa, and Tennessee.
- Indiana University Health Methodist Hospital, a regional facility that utilizes the GRACE Model to provide care management teams that facilitate in-home care to 11,000 Medicare Advantage beneficiaries.
- InterMed, a physician-owned medical group that provides care management services facilitated through a pod structure that fosters trust and continuity for 4,400 Medicare Advantage beneficiaries in Maine.
- Johns Hopkins Medicare Advantage Plan, a payer utilizing care managers and community health workers to care for 5,000 Medicare Advantage beneficiaries in Maryland.
“Each bright spot in this report took advantage of a flexible payment system and adaptive delivery models to engender trust between patients, their care teams, and between team members within care management teams. As a result of everyone sharing information, the team built trust both with each other and with the patients. This trust was crucial for improving health,” said Liaw.
